
Computer Science To English
10 Apr 2018Intro
There are many different types of communities in the world. Sometimes, concepts can get lost in translation when two communities are speaking to each other. These communities can be Computer Science professionals, teachers, firefighters, etc. Each one of these has their own distinct terminologies that can only be understood within the context of that community. So, I have put together a list of terms native to the Computer Science industry.
I will prefix each word with the T for the traditional meaning and CS for the Computer Science meaning. All traditional definitions come from the first definition at dictionary.com unless otherwise noted.
Dictionary
- T Alpha1: The first; beginning.
- CS Alpha: The term used to define the opacity in a color. Example: RGBA refers to the red, green, blue, and alpha in a specific pixel, where alpha represents the transparency.
- T AND: (Used to connect grammatically coordinate words, phrases, or clauses) along or together with; as well as; in addition to; besides; also; moreover.
- CS AND: A logical term in computer science. It is used to determine the truth of a statement. Example: TRUE AND TRUE = TRUE, TRUE AND FALSE = FALSE.
- T Application: The act of putting to a special use or purpose.
- CS Application: A program, typically on a phone or tablet. Examples include: Candy Crush, Groupme, Telegram, etc.
- T Beta: The second letter of the Greek alphabet (β, B).
- CS Beta: The second pre-release of a program. Typically, programs have an alpha phase, which is the first release, then a beta phase, which is the second release, and then they are actually released for public use.
- T Bit2: The mouthpiece of a bridle, having fittings at each end to which the reins are fastened.
- CS Bit: The smallest piece of memory that a computer can hold. A brief overview of computer memory:
4 bits = 1 byte
8 bytes = 1 word
1024 bytes = 1 kilobyte
1024 kilobytes = 1 megabyte
1024 megabytes = 1 gigabyte
1024 gigabytes = 1 terabyte
- T Bug3: (Loosely) any insect or insectlike invertebrate.
- CS Bug: A problem with a program. In other words, a program misbehaves and does not do what it was created to do. The term was coined when diagnosing a problem with one of the first computers. This particular computer was the size of an entire room and was misbehaving. When they finally found out what was causing the problem, it was because an actual insect had gotten caught in the computer.
 You can see how a bug could get stuck in this.
You can see how a bug could get stuck in this.
- T Bite: To cut, wound, or tear with the teeth
- CS Byte: Although these two words are different, they are pronounced the same and could be misinterpreted when someone is speaking. A byte is a piece of computer memory that consists of 8 bits.
- T Character: The aggregate of features and traits that form the individual nature of some person or thing.
- CS Character: A symbol that is represented using a hexadecimal number. Examples include: * $ d 1 . )
So a character in computer science is any symbol used in languages.
 Characters
Characters
- T Class: A number of persons or things regarded as forming a group by reason of common attributes, characteristics, qualities, or traits; kind; sort.
- CS Class: The traditional definition actually does the term class some justice as it is used in Computer Science. Typically though, when referring to a class in Computer Science, it refers to an abstract group from which you can derive an ‘object’, or instance. For example, in a video game you could have a Dog Class, from which you can instantiate, or create, an individual dog. The individual dog can have its own name, breed, owner, etc. but it is still a dog at its core.
- T Code: A system for communication by telegraph, heliograph, etc., in which long and short sounds, light flashes, etc., are used to symbolize the content of a message.
- CS Code: The language that a programmer will create a program in. Examples: CSS, Javascript, R, Python, Java…
- T Editor: A person having managerial and sometimes policy-making responsibility related to the writing, compilation, and revision of content for a publishing firm or for a newspaper, magazine, or other publication.
- CS Editor: A program that highlights key words according to the programming language being written on it. It also can give auto-complete statements, and help streamline the programming process.
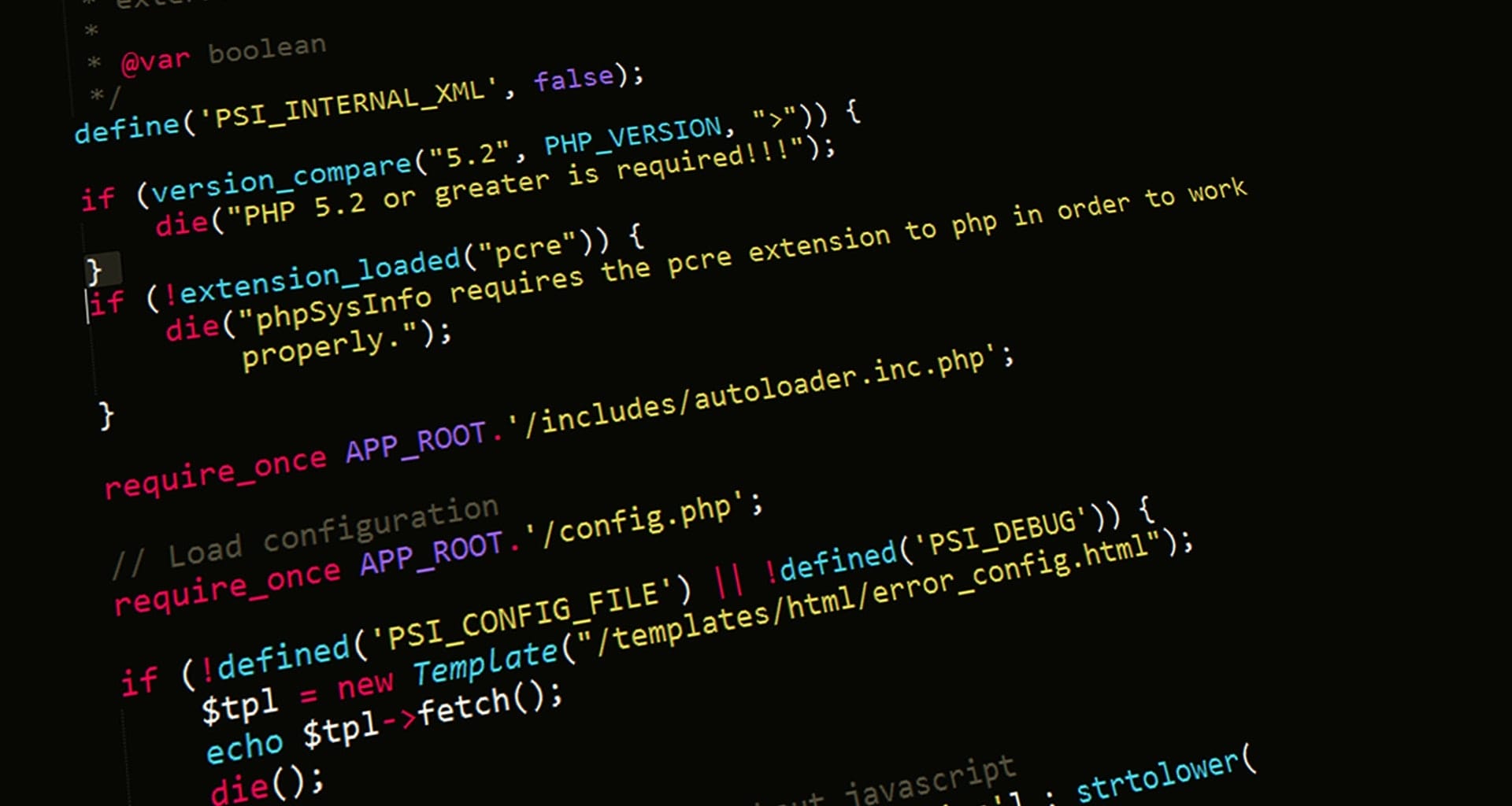 A programming text editor
A programming text editor
- T FAT: Having too much flabby tissue; corpulent; obese.
- CS FAT: File Allocation Table. In other words it is a file system that was created for the Windows Operating System.
- T Function The kind of action or activity proper to a person, thing, or institution; the purpose for which something is designed or exists; role.
- CS Function An abstraction of a set of instructions. For example, you could have a function SquareRoot(x) which returns the square root of x, but it abstracts, or hides the specific way of how it does it.
- T GNOME: (In folklore) one of a species of diminutive beings, usually described as shriveled little old men, that inhabit the interior of the earth and act as guardians of its treasures; troll.
- CS GNOME: A free and open source operating system. This basically means that it is an alternative operating system, like Windows, Mac OS, Ubuntu, etc., except the source code is available for anyone to download and edit.
- T Interface: A surface regarded as the common boundary of two bodies, spaces, or phases.
- CS Interface: An implementation of undefined functions. For example, when programming a game, there is an interface called runnable. To implement this interface, you simply inherit the class, and then implement all the functions.
- T Java4: (Usually lowercase) Slang. coffee.
- CS Java: A computer programming language. This language in particular is useful because it runs mostly the same across all platforms.
 Java
Java
- T Kernel: The softer, usually edible part contained in the shell of a nut or the stone of a fruit.
- CS Kernel: This part is the part that controls how the computer manages all the different programs running at the same time on your computer. This means that it is the center of the whole operating system on any computer.
- T Lamp: Any of various devices furnishing artificial light, as by electricity or gas.
- CS LAMP: Linux, Apache, MySql, PHP. This is a bundle of software that is used in conjunction to program databases.
- T Object: Anything that is visible or tangible and is relatively stable in form.
- CS Object: This is actually quite the opposite of the traditional meaning. An object in programming is an abstract idea of an instantiation of a class. In other words, imagine there is a Dog class, when you create an instance of that class, that is an ‘object’ of the dog class.
- T Patch: A small piece of material used to mend a tear or break, to cover a hole, or to strengthen a weak place.
- CS Patch: Generally a programming fix. In other words, when there is a problem with a program and the creators release a new version, they will release a ‘patched’ version that has fixed the error.
- T Python: Any of several Old World boa constrictors of the subfamily Pythoninae, often growing to a length of more than 20 feet (6 meters): the Indian python, Python molurus, is endangered.
- CS Python: Another programming language. This one is useful for beginners. It has a very English way of writing things. For example, the statement if ‘j’ in ‘john’… will check if j is in John and do something if it is.
- T Ruby: A red variety of corundum, used as a gem.
- CS Ruby: Yet another programming language. This one is much like Python in its simplistic style.
 A gem, similar to a Ruby
A gem, similar to a Ruby
- T Stack: A more or less orderly pile or heap.
- CS Stack: A data structure that simulates a stack in real life. It holds an abstraction of data that you can add more data to the ‘top’ of the stack, or ‘pop’ the top item off the stack.
- T String: A slender cord or thick thread used for binding or tying; line.
- CS String: A composition of ‘characters’ (see above) that forms one string. It is similar to a word in written English. Examples: ‘This is a string’, ‘!#@$#’
- T Thread: A fine cord of flax, cotton, or other fibrous material spun out to considerable length, especially when composed of two or more filaments twisted together.
- CS Thread: A thread in a computer is like a task that is trying to run. A computer has several task vying for run time on the CPU, and a single thread represents one of these tasks. This is an extreme abbreviation of the concept, because the actual concept goes much deeper.
- T Web: Something formed by or as if by weaving or interweaving.
- CS Web: A slang term used to define the Internet.
- T Window: An opening in the wall of a building, the side of a vehicle, etc., for the admission of air or light, or both, commonly fitted with a frame in which are set movable sashes containing panes of glass.
- CS Window: A program’s space that occupies a part of a computer screen.
Conclusion
So, as you can see, this list is not comprehensive. But, it covers the most common Computer Science terms that you will encounter when speaking to a Computer Scientist. Hopefully you can use this to decipher some of what they are trying to tell you, but most likely it will be a challenge. Computer Scientists tend to be very abstract!
Citations
- The third definition on dictionary.com for alpha.
- The second definition on dictionary.com for bit.
- The second definition on dictionary.com for bug.
- The second definition on dictionary.com for java.